cathodic protection junction box distance to pipeline Cathodic protection is a popular protection method for preventing corrosion in pipelines, offshore oil platforms and other steel structures. However, to be implemented effectively, it is crucial to understand the basic principles of . What I find is the best er Genesis II Smoker Box Setup. Allowing easy access to the smoker box, ensuring it stays hot and providing good cooking space.Us.
0 · cathodic protection wiring guide
1 · cathodic protection underground pipeline
2 · cathodic protection structure
3 · cathodic protection pipeline
4 · cathodic protection installation
5 · cathodic protection circuit diagram
6 · cathodic protection calculations
7 · cathodic metal protection process
For the lobby of 10 St. James, Weiss craftsmen created individual frames for each piece of onyx and then secured the single frames into a final supporting frame to accomplish the project. In this way, a single piece of onyx may be removed if there is ever a problem with stone breakage. Weiss worked closely with the contractor to make a supporting
The principal methods for mitigating corrosion on underground pipelines are coatings and cathodic protection (CP). Coatings normally are intended to form a continuous film of .
Cathodic protection systems prevent corrosion of pipelines, above ground storage tank bottoms, plant piping and many other buried or submerged steel metallic structures. A major concern for operators of these assets is extending their . Cathodic protection is a popular protection method for preventing corrosion in pipelines, offshore oil platforms and other steel structures. However, to be implemented effectively, it is crucial to understand the basic principles of .
On-site survey provides vital basis for designing cathodic protection for buried pipelines. A scope of investigation would typically comprise: Environmental considerations: Pipeline route inspection, soil resistivity profile, corrosivity, .
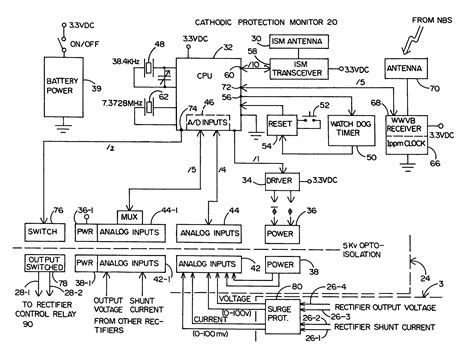
The current output of the individual anodes is determined by measuring the voltage drop across the shunts in the anode junction box. The rectifier current output can be adjusted with fine and coarse tap settings to . Therefore, it is important to locate the most conductive subsurface within the ICCP site. There are two geophysical tests you can use to determine resistivity and the best location for the groundbed: electrical resistivity imaging .The main purpose of a cathodic protection (CP) test station is to provide an access point to terminate cables from a buried structure (pipeline) to take electrical measurements or readings .As long as the electric current flows from the pipeline through the rectifier to the anode bed, as shown in the diagram, exposed pipe metal is protected from corrosion. The distance between .
Farwest standard anode junction boxes provide a low-cost solution to consolidate multiple impressed current anode cables and a means for monitoring individual anode currents. Build to last, these junction boxes include a Hoffman powder .Cathodic Protection is an industrial technique for controlling metallic corrosion. Cathodic protection is commonly used on buried and submerged metallic structures like pipelines, underground storage tanks, locks, subsea equipment, offshore floaters, harbors, and ship hulls.
The principal methods for mitigating corrosion on underground pipelines are coatings and cathodic protection (CP). Coatings normally are intended to form a continuous film of electrically insulating material over the metallic surface to be protected.
cathodic protection wiring guide
cathodic protection underground pipeline
4 in. 30.3 cu. in. metallic square box
Cathodic protection systems prevent corrosion of pipelines, above ground storage tank bottoms, plant piping and many other buried or submerged steel metallic structures. A major concern for operators of these assets is extending their service life. Cathodic protection is a popular protection method for preventing corrosion in pipelines, offshore oil platforms and other steel structures. However, to be implemented effectively, it is crucial to understand the basic principles of bimetallic/galvanic corrosion.On-site survey provides vital basis for designing cathodic protection for buried pipelines. A scope of investigation would typically comprise: Environmental considerations: Pipeline route inspection, soil resistivity profile, corrosivity, interfacial issues, topography, adjacent structure.
The current output of the individual anodes is determined by measuring the voltage drop across the shunts in the anode junction box. The rectifier current output can be adjusted with fine and coarse tap settings to optimize the polarization of the protected structure. Therefore, it is important to locate the most conductive subsurface within the ICCP site. There are two geophysical tests you can use to determine resistivity and the best location for the groundbed: electrical resistivity imaging (ERI) or the ASTM G57 soil test. ERI Vs. ASTM G57: Differences & Similarities.The main purpose of a cathodic protection (CP) test station is to provide an access point to terminate cables from a buried structure (pipeline) to take electrical measurements or readings on that structure.
As long as the electric current flows from the pipeline through the rectifier to the anode bed, as shown in the diagram, exposed pipe metal is protected from corrosion. The distance between rectifier units depends on the current requirements of the system. Current requirements are based on diferent soil types.Farwest standard anode junction boxes provide a low-cost solution to consolidate multiple impressed current anode cables and a means for monitoring individual anode currents. Build to last, these junction boxes include a Hoffman powder coated steel enclosure, a Micarta insulating panel, copper buss bar, shunts (customer selected), and .
Cathodic Protection is an industrial technique for controlling metallic corrosion. Cathodic protection is commonly used on buried and submerged metallic structures like pipelines, underground storage tanks, locks, subsea equipment, offshore floaters, harbors, and ship hulls.
The principal methods for mitigating corrosion on underground pipelines are coatings and cathodic protection (CP). Coatings normally are intended to form a continuous film of electrically insulating material over the metallic surface to be protected.Cathodic protection systems prevent corrosion of pipelines, above ground storage tank bottoms, plant piping and many other buried or submerged steel metallic structures. A major concern for operators of these assets is extending their service life. Cathodic protection is a popular protection method for preventing corrosion in pipelines, offshore oil platforms and other steel structures. However, to be implemented effectively, it is crucial to understand the basic principles of bimetallic/galvanic corrosion.
On-site survey provides vital basis for designing cathodic protection for buried pipelines. A scope of investigation would typically comprise: Environmental considerations: Pipeline route inspection, soil resistivity profile, corrosivity, interfacial issues, topography, adjacent structure. The current output of the individual anodes is determined by measuring the voltage drop across the shunts in the anode junction box. The rectifier current output can be adjusted with fine and coarse tap settings to optimize the polarization of the protected structure. Therefore, it is important to locate the most conductive subsurface within the ICCP site. There are two geophysical tests you can use to determine resistivity and the best location for the groundbed: electrical resistivity imaging (ERI) or the ASTM G57 soil test. ERI Vs. ASTM G57: Differences & Similarities.The main purpose of a cathodic protection (CP) test station is to provide an access point to terminate cables from a buried structure (pipeline) to take electrical measurements or readings on that structure.
As long as the electric current flows from the pipeline through the rectifier to the anode bed, as shown in the diagram, exposed pipe metal is protected from corrosion. The distance between rectifier units depends on the current requirements of the system. Current requirements are based on diferent soil types.
4 inch square box metal studs drywall
cathodic protection structure
This stainless steel box can be placed under the grill grates to be as close to your heat source as possible, keeping your wood chips and chunks fuming along with your foods. Infuse your saucy ribs with hickory smoke, match maple flavors with grilled turkey, or add fruity applewood chips to pork tenderloin.Check it out on Amazon Cave Tools have been making high quality, specialist grilling equipment for years, so it stands to reason that this beauty sits at the top of my list. It measures three by nine inches and can hold up to two cups of wood chips. This is more than enough to house a good amount of wood chips to turn . See more
cathodic protection junction box distance to pipeline|cathodic protection structure